Company Administration Explained: What Occurs When Services Go into Liquidation?
Company Administration Explained: What Occurs When Services Go into Liquidation?
Blog Article
The Process and Repercussions of a Company Entering Administration
As a business faces economic distress, the decision to get in management marks an essential point that can have far-ranging implications for all entailed celebrations. The procedure of entering management is intricate, entailing a series of actions that aim to browse the firm towards possible healing or, in some instances, liquidation.
Summary of Firm Administration Process
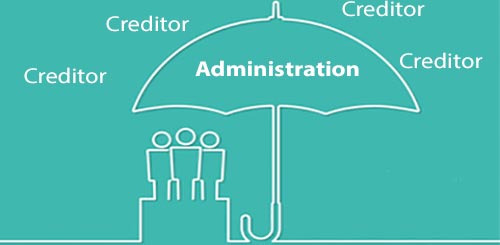
In the world of corporate restructuring, a crucial preliminary action is acquiring a thorough understanding of the elaborate firm administration procedure. Firm administration refers to the formal bankruptcy procedure that aims to save a financially distressed business or attain a better result for the business's financial institutions than would be possible in a liquidation scenario. This procedure entails the appointment of an administrator, who takes control of the business from its supervisors to assess the economic scenario and determine the most effective training course of activity.
Throughout management, the company is given security from lawful activity by its financial institutions, offering a halt duration to formulate a restructuring plan. The administrator collaborates with the company's monitoring, creditors, and other stakeholders to develop a method that might include offering the company as a going concern, reaching a company volunteer setup (CVA) with creditors, or eventually positioning the firm right into liquidation if rescue efforts verify futile. The main goal of business administration is to optimize the go back to lenders while either returning the business to solvency or closing it down in an orderly manner.

Duties and Duties of Administrator
Playing a critical role in managing the business's decision-making processes and economic affairs, the administrator presumes significant duties during the company restructuring procedure. The primary obligation of the manager is to act in the finest interests of the firm's lenders, intending to accomplish one of the most beneficial outcome feasible - what happens to employees when a company goes into liquidation. This involves carrying out a comprehensive analysis of the firm's monetary situation, establishing a restructuring strategy, and executing approaches to optimize returns to financial institutions
Furthermore, the manager is accountable for liaising with numerous stakeholders, including staff members, vendors, and regulatory bodies, to make sure openness and conformity throughout the administration procedure. They should additionally communicate successfully with investors, offering routine updates on the firm's progression and seeking their input when necessary.
Additionally, the manager plays an essential function in taking care of the everyday operations of business, making vital choices to maintain continuity and preserve value. This includes assessing the stability of various restructuring options, negotiating with creditors, and eventually assisting the business towards a successful departure from administration.
Effect on Business Stakeholders
Presuming an important position in managing the business's decision-making processes and financial affairs, the administrator's actions during the company restructuring procedure have a straight influence on different company stakeholders. Shareholders may experience a decline in the worth of their financial investments as the firm's economic problems are addressed. Financial institutions, including lending institutions and distributors, may deal with uncertainties relating to the settlement of financial obligations owed to them. Staff members commonly run into task insecurities due to potential layoffs or modifications in work conditions as part of the restructuring efforts. Clients might experience disturbances in services or product schedule throughout the administration procedure, impacting their count on and commitment in the direction of the firm. Additionally, the area where the business operates could be impacted by possible task losses or changes in the company's procedures, affecting neighborhood economic situations. Efficient communication from the administrator to stakeholders is critical in handling expectations, reducing concerns, and cultivating transparency throughout the administration process.
Lawful Effects and Obligations
Throughout the procedure of business management, careful factor to consider of the lawful effects and responsibilities is vital to ensure conformity and shield the passions of all stakeholders entailed. When a firm gets in administration, it causes a collection of lawful requirements that must be complied with. Among the main commitments is for the appointed administrator to act in the finest interests of the business's lenders. This task requires the administrator to perform comprehensive investigations right into the business's events, assess its monetary position, and create a method to optimize go back to financial institutions.
Furthermore, lawful ramifications arise worrying the therapy of staff members. The administrator needs to comply with work legislations relating to redundancies, staff member rights, and commitments to supply essential information to employee agents. Failing to abide with these legal needs can lead to lawsuit versus the firm or its managers.
Furthermore, the business going into management may have contractual responsibilities with different parties, including customers, property managers, and suppliers. These agreements require to be evaluated to determine the most effective program of activity, whether to terminate, renegotiate, or satisfy them. Failing to take care of these contractual commitments appropriately can bring about conflicts and potential legal repercussions. Essentially, understanding and meeting lawful commitments are vital facets of navigating a firm via the administration process.
Strategies for Business Recovery or Liquidation
In considering the future direction of a firm in administration, critical planning for either recovery or liquidation is vital to chart a sensible course ahead. When going for business recovery, essential techniques may consist of conducting an extensive analysis of the service operations to recognize inefficiencies, renegotiating leases or contracts to boost capital, and implementing cost-cutting actions to boost success. In addition, looking for new financial click here for more investment or funding alternatives, branching out income streams, and focusing on core proficiencies can all add to a successful recovery plan.
Verdict
Finally, the procedure of a company going into management entails the appointment of a manager, who handles the responsibilities of handling the company's affairs. This procedure can have considerable repercussions for various stakeholders, consisting of shareholders, financial institutions, and staff members. It is essential for companies to very carefully consider their alternatives and approaches for either recovering from economic problems or waging liquidation in order to reduce prospective legal implications and commitments.
Company administration refers to the formal insolvency procedure that aims to rescue a financially distressed firm or accomplish a much better outcome for the firm's lenders than would be possible in a liquidation scenario. The manager works with the business's administration, creditors, and other stakeholders to design an approach that may entail selling the organization as a going issue, reaching a company voluntary setup (CVA) with financial institutions, or ultimately positioning the company into liquidation official site if rescue efforts prove futile. The main objective of business management is to maximize the return to financial institutions while either returning the business to solvency or closing it down in an organized way.
Assuming a critical setting in managing the firm's economic affairs and decision-making processes, the manager's activities during the corporate restructuring process have a direct impact on different firm stakeholders.In verdict, the procedure of a firm going into administration includes the appointment of a manager, who takes on the responsibilities of managing the company's events.
Report this page